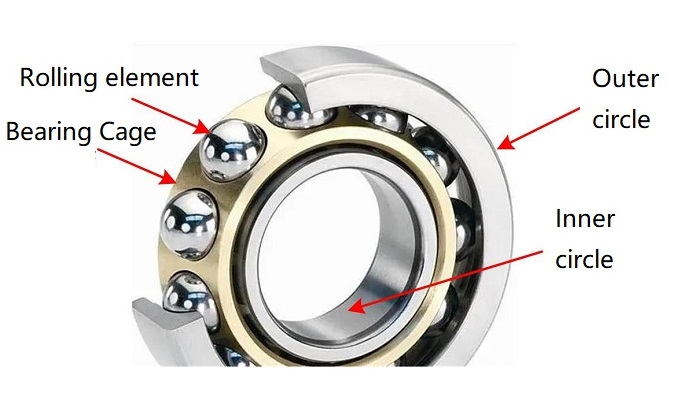
The specific production process of bearings is as follows: raw materials - inner and outer ring machining, steel ball or roller machining, cage (stamping or solid) machining - bearing assembly - finished bearings.
In the bearing production process, the most critical stages are as follows:
1. Forging Stage
The forging stage is crucial in ensuring bearings' reliability and lifespan. After forging, the raw materials form rough bearing blanks. At the same time, the material's structure becomes denser and more streamlined, improving bearing reliability and lifespan. Additionally, the quality of the forging process directly affects the material utilization rate, affecting production costs.
2. Heat Treatment Stage
The heat treatment stage involves subjecting the forged and machined bearing blanks to high-temperature treatment. It directly affects the uniformity of carbon diffusion in the bearing blanks, enhancing wear resistance and hardness, and is crucial for ensuring the reliability and lifespan of bearings.
3. Grinding Stage
After heat treatment, the bearing blanks undergo grinding, essential for maintaining bearing precision. After the grinding stage, the production of bearing blanks is essentially completed.
The inner and outer bearing rings process includes rod or tube material - forging - machining - heat treatment - grinding - superfinishing - component final inspection - rust prevention and storage.
Key production equipment includes cold rolling machine, fully automatic ball bearing inner ring grinding machine, quenching line, annealing furnace, press, CNC lathe, bearing grinding machine, inner groove grinding machine, outer groove grinding machine, high-precision horizontal spindle surface grinder, CNC milling machine, centerless grinder, precision groove superfinishing machine, inner surface CNC grinding machine, CNC reciprocating double-end face grinder, high-temperature high-speed bearing test machine, heat treatment production line, and quality inspection equipment.
The basic production process of rolling bearings varies depending on the type, structural form, tolerance level, technical requirements, materials, and batch size.
The processing processes for various bearing components are as follows:
Processing of Bearing Rings:
Bearing inner and outer rings may differ depending on the original material or blank form. The process generally includes rod or tube material (some may require forging and annealing or normalizing) - machining - heat treatment - grinding - superfinishing or polishing - component final inspection - rust prevention - storage - (pending assembly of matched parts).
Processing of Steel Balls:
The processing of steel balls also varies based on the state of the original material. The process includes bar stock or wires cold heading (some bar stock may require cold heading, ring cutting, and annealing) - rough turning, rough grinding, soft grinding, or polishing - heat treatment - hard grinding - precision grinding - superfinishing or grinding - component grouping for final inspection - rust prevention, packaging - storage (pending assembly of matched parts).
Processing of Rollers:
The processing of rollers depends on the type of original material. The process includes bar stock machining or wire drawing, followed by forming ring grooves and soft grinding - heat treatment - soft spot formation - rough grinding of outer diameter - rough grinding of end faces - end face grinding - fine outer diameter grinding - final outer diameter grinding - component grouping for final inspection - rust prevention, packaging - storage (pending assembly of matched parts).
Processing of Cages
The processing of cages varies based on design and material. It can be classified into two categories:
(1) Sheet material → shearing → punching → stamping forming → shaping and precision machining → pickling or shot blasting → final inspection → rust prevention, packaging → storage (pending assembly of matched parts).
(2) Solid cage processing: The processing of solid cages varies depending on the original material or blank form. The process includes bar stock, tube material, forgings, or castings → inner diameter, outer diameter, end face, chamfer machining → drilling (or reaming, boring) → pickling → final inspection → rust prevention, packaging → storage (pending assembly of matched parts).
Assembly Process for Rolling Bearings:
After inspection for demagnetization and cleaning, the components of rolling bearings, such as inner rings, outer rings, rollers, and cages, proceed to the assembly workshop. The process is as follows:
Demagnetization, cleaning → sorting and selecting inner and outer ring groove dimensions → matching assembly → clearance inspection → riveting the cage → final inspection → demagnetization, cleaning → rust prevention, packaging → storage (boxing, shipping).
Summary
The production process of bearings encompasses crucial steps such as forging, heat treatment, and precision grinding. Forging and heat treatment directly impact the reliability and lifespan of bearings, while precision grinding is essential for ensuring their accuracy. Different bearing components, such as inner and outer rings, steel balls, rollers, and cages, undergo distinct machining processes tailored to their respective materials and design specifications. Ultimately, these components undergo rigorous inspection and assembly processes to form finished bearings, guaranteeing their quality and performance. The entire bearing production process relies on precision equipment and strict quality control measures to meet the diverse demands of industrial applications.