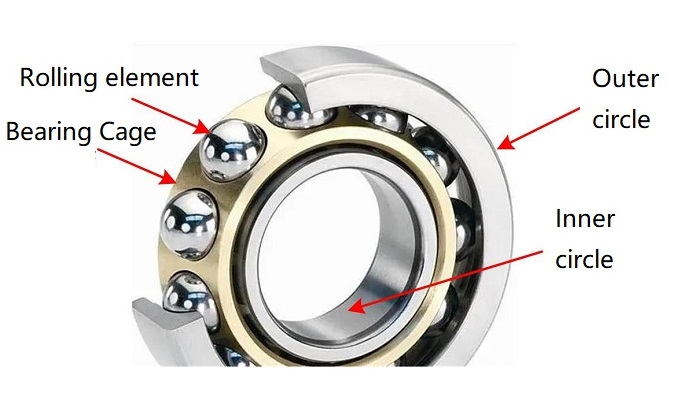
What is Linear Bearing?
Linear bearings are important components in many industrial machines and equipment. They provide smooth, low-friction motion in a linear direction and can support high loads with minimal wear and tear. These bearings come in different types, such as ball, roller, and plain bearings, each with unique features and benefits. Compared to flange bearings, linear bearings are designed specifically for linear motion and provide superior performance and accuracy.
What is the Importance of Linear Bearings?
Linear bearings are essential components in machinery and equipment that require linear motion, such as CNC machines, 3D printers, medical equipment, and automation systems. They allow for smooth and precise movement of components along a linear path, reducing friction and wear and tear on the machinery.
Linear bearings provide numerous benefits, including increased accuracy, reduced vibration and noise, and improved durability. They also help increase the speed and efficiency of machinery and reduce maintenance and downtime costs.
Without linear bearings, machines would not be able to perform their intended functions with the same level of precision and reliability. Applied In industries such as manufacturing, aerospace, and automotive, where high accuracy and reliability are essential, it needs linear bearings to keep precision.
How do Linear Bearings Work?
Linear bearings operate through a rolling element, typically a ball or roller, along a track or rail. This element is contained in a cage or retainer to maintain an even spacing and prevent dislodging. The path or rail is usually made of hardened steel, designed to be straight and smooth, minimising friction and wear. Applying a force to the rolling element allows it to roll along the track or rail, resulting in the smooth and efficient movement of the linear bearing. The rolling feature also helps to distribute the load evenly across the length of the track or rail, reducing wear and extending the life of the path. This design allows linear bearings to provide reliable, low-friction motion in various applications, from manufacturing equipment to home appliances.
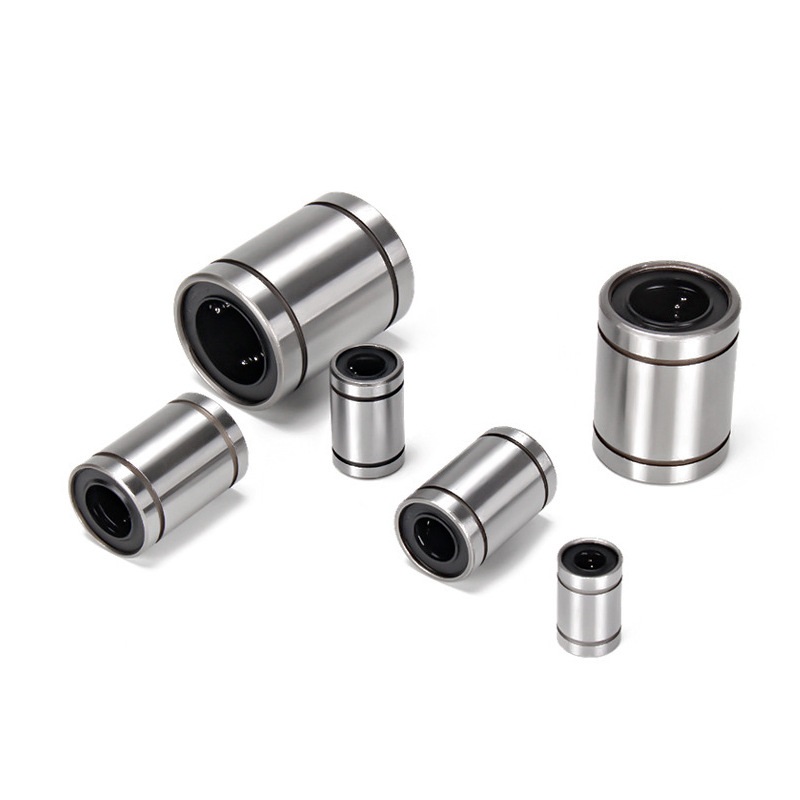

Types of Linear Bearings
Ball Bushing Bearings:
Also known as linear ball bearings, they are the most commonly used. These bearings use recirculating ball bearings that move along the shaft and inside the housing to provide smooth and accurate linear motion. The ball bearings are held in place by a cage or retainer that keeps them evenly spaced, preventing them from rubbing against each other and reducing friction. Ball bushing bearings are available in several types, closed, open, and adjustable, to suit different applications and operating environments in applications that require high precision and accuracy, such as machine tools, robotics, and automation systems.
Ball Bushing
Round Rail Bearings:
Round Rail Bearings are linear bearings that use cylindrical rollers instead of balls. They are designed for high load capacity and stiffness and are commonly used in heavy-duty applications such as machine tools and material handling equipment. The rollers in a round rail bearing are arranged in a circular pattern, allowing them to distribute loads evenly and provide smooth, consistent linear motion. They also have a longer operating life than ball bushing bearings due to their ability to handle higher loads and resist wear and fatigue.
Slide Bearings:
Also known as plain or sleeve bearings, they are a type of linear bearing that uses a sliding mechanism rather than a rolling element. The sentence in active voice would be: Two parts constitute them: a stationary bearing shell and a sliding bearing surface, which people can make of various materials like bronze, graphite, or plastic. The sliding bearing surface is lubricated to reduce friction and wear.
People often use slide bearings in low-load applications where precision and accuracy are not critical. They are known for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness compared to other types of linear bearings. However, slide bearings may have load capacity and speed limitations and may require periodic maintenance to ensure proper lubrication.
Cam Roller Guides:
They are using a series of cam rollers instead of balls or rollers. These cam rollers are arranged in a circular pattern, providing smooth and precise linear motion. People often use Cam Roller Guides in high-load applications because they can support heavy loads and resist deformation. They are also known for their high accuracy and stiffness, which makes them suitable for applications that require precise positioning and repeatability. People commonly use Cam Roller Guides in machine tools, robotics, and automation equipment.
Cam Bearing
Linear Needle Roller Bearings:
It’s a type of linear bearing that use needle-shaped rollers to provide smooth and accurate linear motion. People design them to handle high speeds and high precision applications where the load capacity required is relatively low. They can also provide high accuracy and repeatability, making them a popular choice in the medical, semiconductor, and aerospace industries. However, they may require frequent maintenance due to their small size and delicate nature.
Needle Roller Bearing
Linear Air Bearings:
Also known as aerostatic bearings, they use a thin layer of compressed air to provide a virtually frictionless and vibration-free linear motion. They are often used in high-precision and high-speed applications, such as semiconductor manufacturing equipment and optical inspection machines. Linear Air Bearings can achieve ultra-precision and repeatability due to their ability to maintain a constant gap between the bearing and the track, regardless of load or speed. However, they require a clean and dry environment to prevent contamination and may require more maintenance than other linear bearings.
Magnetic Bearings:
These bearings use magnetic fields to provide smooth and precise linear motion. They are often used in applications requiring high precision and frictionless movement.
It's worth noting that while magnetic bearings can provide exact and smooth linear motion, they are typically more complex and expensive than other types of linear bearings. They also require a power source to generate the magnetic fields needed to support the load, which can be a drawback in specific applications. Magnetic bearings are often used in high-speed applications, such as semiconductor manufacturing and aerospace engineering.
Different types of linear bearings have various features to use. The choice of the linear bearing depends on the application's specific requirements, such as load capacity, precision, speed, and environmental factors. Here is the article about 12 tips for choosing a linear bearing, that could help you to choose the right linear bearing best.
Most Common Problems When Using Linear Bearings
Linear bearings are widely used in industrial applications due to their smooth and efficient linear motion. However, like any mechanical component, they can encounter problems during operation. Here are some of the most common issues when using linear bearings:
Contamination: Linear bearings can be affected by dirt, dust, or other contaminants, which can cause wear, damage, and reduced performance. Proper sealing and regular cleaning can help prevent contamination.
Misalignment: Linear bearings can be affected by misalignment between the rail and the bearing, which can cause uneven wear and reduced performance. Proper installation and alignment can help prevent misalignment.
Overloading: Excessive loads can affect Linear bearings, which can cause premature wear and failure. Proper selection of the bearing and rail based on the load and application can help prevent overloading.
Corrosion: Linear bearings can be affected by exposure to harsh environments or chemicals, which can cause wear and reduced performance. Proper selection of materials and coatings can help prevent corrosion.
Lubrication: Linear bearings require proper lubrication to reduce friction and wear. Improper lubrication or lack of lubrication can cause premature wear and failure.
Installation: Improper installation of linear bearings can cause misalignment, improper preload, and other problems that can affect performance and cause premature wear and failure.
Proper maintenance, installation, and selection of the appropriate linear bearing and rail for the application can help prevent these common problems and ensure optimal performance and longevity.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Linear Bearings?
Advantages:
●Smooth and accurate linear motion: Linear bearings provide smooth and precise linear motion, making them ideal for applications that require high accuracy and precision. They also help reduce vibration and noise, improving overall performance.
●High load capacity: Linear bearings can support high loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty and high-performance motion control applications.
●Low friction and wear: Linear bearings use rolling elements to minimize friction and wear. It reduces the need for lubrication and helps to extend the life of the bearing.
●Easy to install and maintain: Linear bearings are relatively easy to install and maintain, making them a cost-effective solution for many applications. They also require less space than other types of bearings, which can be crucial in specific applications.
●Available in various types and sizes to fit different applications: Linear bearings are available in multiple styles, including ball bushing bearings, round rail bearings, slide bearings, cam roller guides, linear needle roller bearings, linear air bearings, and magnetic bearings. They are also available in different sizes, making finding the right bearing for a specific application easier.

Disadvantages:
◆Cost: Linear bearings can be more expensive than other types, especially if they need to be customized or have specific requirements for a particular application.
◆Alignment and lubrication: Linear bearings require proper alignment and lubrication to function effectively. Improper alignment or inadequate lubrication can cause excessive wear, noise, vibration, and premature failure.
◆Noise and vibration: In some applications, linear bearings can produce noise or vibration if improperly installed or maintained. It can be an issue in applications where noise and vibration are critical factors.
◆Maintenance: Linear bearings may require frequent cleaning and maintenance in harsh environments. For example, exposure to dust, dirt, moisture, or corrosive substances can lead to premature wear or failure of the bearing.
◆Installation: Proper installation of linear bearings can be critical to their performance and longevity. In some cases, ensuring proper alignment and fit may require specialized tools or expertise.
What Kinds of Industries Need to Use Linear Bearing?
Linear bearings are widely used across various industries that demand smooth and precise linear motion control. These industries include manufacturing, aerospace, medical, packaging, automotive, construction, and agriculture.
Manufacturing: Facilities employ linear bearings in CNC machines, assembly lines, and robotics to achieve reliable and precise motion control.
Aerospace: linear aircraft and aerospace equipment bearings due to their high load capacity and precise motion control, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Medical equipment: such as X-ray machines, CT scanners, and MRI machines utilize linear bearings to provide smooth and accurate motion control, allowing for proper diagnoses and treatment.
Packaging equipment: such as filling machines, labelling machines, and sealing machines use linear bearings for their high speed and precision.
Automotive: linear bearings are essential components in the automotive used in suspension, steering, and transmission systems for their durability and precision.
Construction: including cranes and excavators, use linear bearings due to their ability to withstand heavy loads and provide precise motion control.
Agricultural equipment: tractors and harvesters benefit from linear bearings' ability to withstand harsh environments and provide smooth motion control.
Overall, linear bearings are an ideal solution for industries that require precise and smooth linear motion control, high load capacity, and durability.