Linear guides, also known as linear slides, are widely used in applications requiring high precision or high-speed linear reciprocating motion, and they can withstand a certain amount of torque. Their role is to support and guide moving components, enabling them to move in a straight line according to a given direction. Selecting the appropriate linear guide involves considering multiple aspects. This article will introduce how to choose the right linear guide for your needs from different dimensions.
Tip 1: Types and Features
Currently, common types of linear guides include ball linear guides, roller linear guides, and cylindrical linear guides. They have different characteristics and application ranges, which can be chosen based on their features:
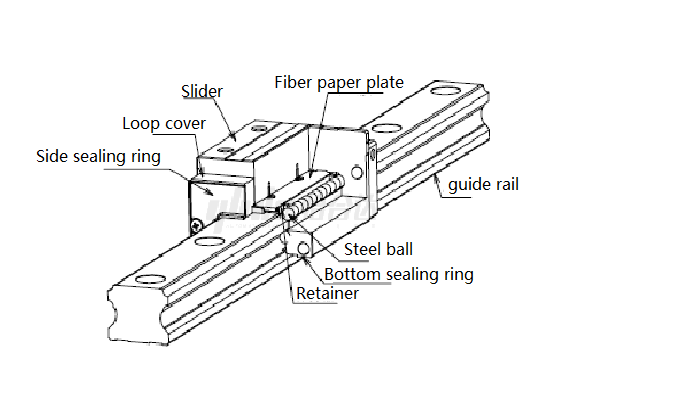
Ball linear guide rail:
(1) High precision
(2) High load-bearing capacity
(3) High rigidity in all directions but higher cost

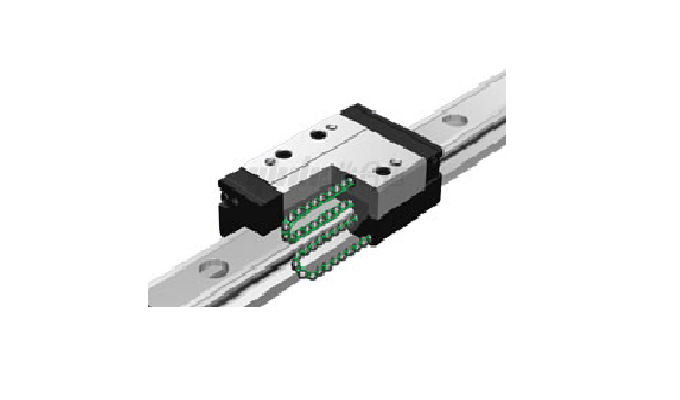
Roller linear guide rail:
(1) High speed, low noise
(2) Corrosion-resistant and not easily rusted
(3) Simple maintenance and easy replacement
(4) Small errors, good precision
(5) Light load
(6) Maximum precision is insufficient
(7) Relatively limited application range
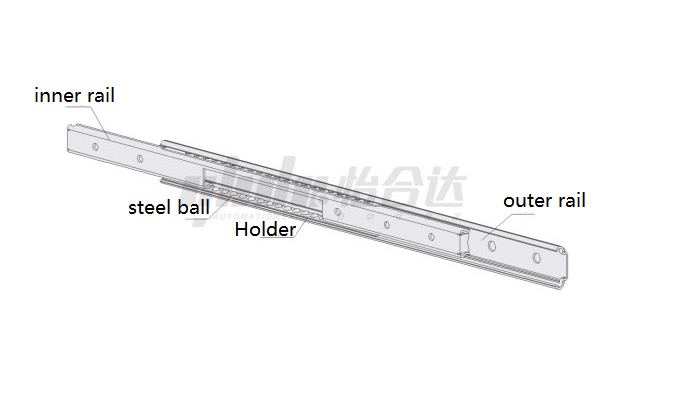
Cylindrical linear rail:
(1) Cylindrical sliders suitable for special occasions
(2) Have self-aligning ability
(3) Inexpensive
(4) Low precision
Tip 2: Key Parameters
When selecting linear guide rails, various parameters need to be considered, including:
Operating conditions: Determine the type of linear guide required based on the processing precision and scope of different machine tools.
Load-bearing capacity: Select a suitable slider based on the load-bearing capacity to ensure that the linear guide can safely support the required weight. The load-bearing capacity also implies how much weight the slider can bear, which relates to the safety factor when the guide is in operation. Generally, manufacturers provide a load safety factor table, and users only need to choose within the specified value.
Expected service life: Consult the supplier to understand the expected service life of the linear guide to ensure stable operation and efficiency of the equipment. Linear guide products with a good service life can maintain stable operation and efficiency of the equipment.

Tip 3: External Form
Based on actual needs, the selection of linear guides can be made based on their external forms, mainly in two types: circular and square:
Circular guide: It is used in conjunction with linear bearings and shafts, appearing cylindrical, and can be assembled in circular holes. At the same time, linear bearings can also be used in conjunction with sliders to achieve flat installation. The installation and use of circular guides are relatively convenient and space-saving.
Square guide: It is used in conjunction with square sliders and square guides, appearing square in shape. Considering friction and load-bearing capacity, the square guide has face-to-face friction with the slider, resulting in greater frictional force and uniform load. However, it requires regular oil lubrication.
In summary, the typical application of square guides is in the machine tool industry, where there are higher requirements for load capacity, rigidity, and accuracy. However, it has high installation requirements and costs. On the other hand, circular guides demonstrate their advantages in this aspect. Even when installed on surfaces with poor flatness, they can still operate smoothly. Generally, circular guides can be installed more quickly and run more smoothly compared to square guides.
Conclusion
Users who need to purchase linear guide products can refer to the above three tips for selection. Additionally, finding reliable and reputable manufacturers is also an essential guarantee for saving time and obtaining high-quality products. Strong performance, professional sales processes, timely and effective communication, and reasonable prices are key conditions for successful transactions.