Trapezoidal screws and ball screws are common types of mechanical transmission devices, each playing a significant role in engineering applications. Their distinct designs and operational principles determine their respective advantages and limitations within their fields. Understanding and correctly applying them can maximize the efficiency and reliability of mechanical systems. This article will delve into a detailed comparison of trapezoidal screws and ball screws in terms of their structural design, performance, and application scenarios, providing engineers and designers with a comprehensive selection guide.
Structural Design and Operational Principles
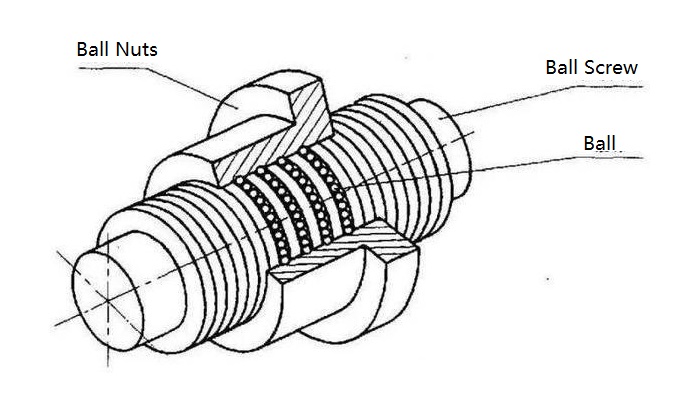
Trapezoidal screws typically feature a trapezoidal thread profile design, with a relatively simple structure and low manufacturing costs. They are commonly used in low-speed high-torque transmission systems, but their friction limits their precision and efficiency. In contrast, ball screws utilize ball bearings and balls for transmission, reducing friction through rolling motion, significantly enhancing transmission efficiency and precision, especially suitable for high-speed transmission and precise positioning applications.
Comparison of Precision and Efficiency
Precision and efficiency are crucial indicators of transmission device performance. Ball screws generally exhibit higher precision and transmission efficiency, as the rolling motion of the balls effectively reduces friction losses, enhancing transmission efficiency. In contrast, the threaded structure of trapezoidal screws leads to higher friction, resulting in generally lower transmission efficiency and precision. Ball screws can offer more precise and stable transmission performance in applications requiring high-precision positioning and greater load-bearing capacity.

Analysis of Load-Bearing Capacity and Service Life
Load-bearing capacity and service life are another key comparative metric. Due to the use of ball bearings, ball screws typically demonstrate higher load-bearing capacity and longer service life, capable of withstanding larger radial and axial loads. Trapezoidal screws, due to higher friction, exhibit relatively lower load-bearing capacity and service life, suitable for applications with lower requirements for precision and transmission.
Selection Strategy for Applications
Choosing the appropriate transmission device is crucial for ensuring the reliability and performance stability of mechanical systems, based on specific application requirements and working environments. Ball screws are an ideal choice for scenarios necessitating high-precision positioning and greater load-bearing capacity. In contrast, trapezoidal screws are more suitable for some low-speed and relatively simple transmission systems. During the engineering design process, a comprehensive assessment of factors such as transmission efficiency, precision, load-bearing capacity, and expected service life is necessary to determine the most suitable transmission device. In specific application scenarios, engineers and designers should customize designs based on system requirements to fully leverage the advantages of the transmission device and achieve stable system operation.
Prospects for the Development Trends of Trapezoidal Screws and Ball Screws
With the continuous development of engineering technology, innovations and improvements in the design and manufacturing of trapezoidal screws and ball screws continue to emerge. The application of new materials, advancements in precision machining technology, and improvements in lubrication and sealing techniques have brought about better performance and extended service life for both types of transmission devices. In the fields of industrial automation and precision manufacturing, the application trend of ball screws is more pronounced, with their high precision, efficiency, and stable performance increasingly favored by more engineers and designers. However, trapezoidal screws still maintain a certain market demand in some simple transmission systems due to their simple structure and low manufacturing costs.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, trapezoidal screws and ball screws each have their own advantages and limitations. When selecting transmission devices, engineers should conduct comprehensive evaluations based on specific application requirements and expected performance indicators. Reasonable selection of transmission devices, while meeting system requirements, can not only improve work efficiency and precision but also extend the service life of mechanical systems and reduce maintenance costs. Therefore, a scientifically and reasonably selected transmission device is of vital significance for ensuring the stable operation of mechanical systems. For further information or any inquiries, please feel free to consult professional engineers in the relevant field.