I. Product Introduction
The belt conveyor is a machine that uses frictional drive to transport materials in a continuous manner. By applying it, a material transportation process can be formed on a certain conveyor line, from the initial feeding point to the final discharging point. It can transport both bulk materials and unitized items. In addition to pure material transportation, it can also be coordinated with the requirements of the technological processes in the production processes of various industrial enterprises to form a rhythmic assembly line transportation line. Therefore, belt conveyors are widely used in various modern industrial enterprises.

II. Overall Structure and Components
Conveyor Belt
The conveyor belt is one of the core components of this conveyor. It has good flexibility and wear resistance, enabling it to carry various materials and transport them smoothly. Its material may be specially treated to adapt to different working environments and material characteristics.
The width and thickness of the conveyor belt are customized according to actual transportation requirements to meet the transportation volume and load - bearing capacity requirements of different materials. A wider conveyor belt is suitable for transporting materials with a larger volume or a larger quantity, while a thicker conveyor belt can withstand greater weight and friction, extending its service life.
Drive Device
The drive device usually includes components such as a motor and a reducer. The motor provides the power source, and the reducer converts the high - speed rotation of the motor into low - speed and high - torque power suitable for the operation of the conveyor belt, ensuring the smooth start - up and operation of the conveyor belt, and at the same time reducing the impact and wear on the conveyor belt.
The power of the drive device is selected according to factors such as the length of the conveyor, the transportation volume, and the weight of the materials, to ensure that the conveyor can operate normally under various working conditions without power shortage or overload.
Support Frame and Support Structure
The support frame and support structure of the conveyor play a role in fixing and supporting the entire conveyor, ensuring its stability and reliability during operation. The support frame is usually made of metal materials, such as steel, which has sufficient strength and stiffness to bear the weight of components such as the conveyor belt, materials, and drive device, as well as various forces generated during the operation.
The support structure includes components such as idlers. The idlers are installed under the conveyor belt to support the conveyor belt and materials, reducing the sag of the conveyor belt and the friction between the materials and the conveyor belt, enabling the conveyor belt to run smoothly. The spacing and arrangement of the idlers are reasonably designed according to the length of the conveyor belt and the characteristics of the materials to ensure that the conveyor belt is evenly stressed and extend the service life of the conveyor belt.

III. Product Features
High Conveying Capacity
It can handle a wide variety of material types and easily meet the different production volume requirements from small - scale production workshops to large - scale industrial bases, providing a solid material transportation guarantee for various production scenarios.
Strong Flexibility
The length can be adjusted arbitrarily according to actual engineering requirements, ranging from a few meters to dozens of kilometers. Loading and unloading operations can be easily carried out at any position on the conveyor line, greatly improving the convenience of material transportation allocation.
Stable Operation
During operation, the relative movement between the materials and the conveyor belt is minimal, making the entire transportation process very stable. In addition, this stable operation mode keeps the power consumption at a low level, achieving efficient and energy - saving transportation operations.
Low Maintenance Cost
The components of the belt conveyor have a high degree of standardization, which makes the replacement and maintenance of parts simple and easy during the equipment maintenance process. Moreover, the number of wearing parts during the normal operation of the equipment is relatively small, further reducing the frequency and cost of maintenance work. From the overall operation perspective, both the human and material resources required for daily maintenance and the long - term equipment repair investment are kept at a low level, saving a large amount of operating costs for enterprises.
Ⅳ. Application Industries and Cases
1. Discharging Conveyor in Automatic Assembly Machine
In an automatic assembly machine, after the products are assembled, they can be discharged through the conveyor, transporting the products to the next working position or outputting and collecting them. (It can also be used for feeding.)

2. Fixture Linear Return Line in Automatic Assembly Machine
- Motor - driven, using imported elastic belts to transport accompanying fixtures, realizing the linear return of fixtures.
- The number of fixture circular workstations can be customized according to customer needs. The transportation speed is stable and adjustable, and there is no noise.
- The mechanism is compact and the appearance is beautiful.
- Reduces the cost of design and manufacturing.
- Can be customized and designed according to different customer needs.

3. Mesh Belt Chain Conveyor for Pallet Stacking and Feeding
In the pallet stacking and feeding device, the mesh belt chain conveyor can be used for the storage of pallets, realizing single - station buffering.

IV. Selection Method
Take the AMT05 - 02A type as an example:
The following is the selection information.
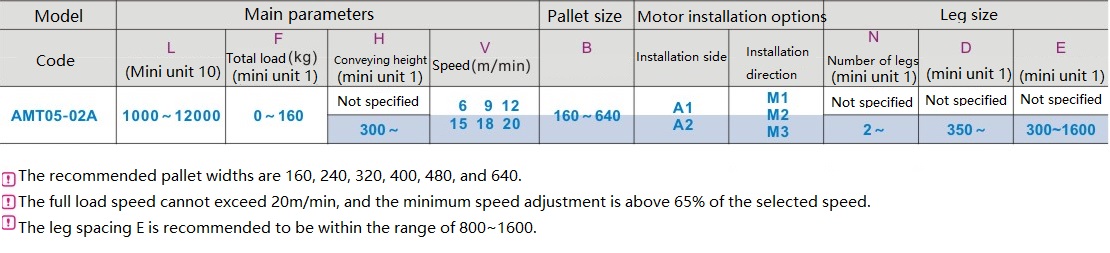

Selection:
According to the selection information, first obtain the parameters you care about, such as length, total load, and speed. Select according to the environment you use.
Example: The selection requirement this time is for material transportation. The length (L) required is 3000MM, the load (F) is 60kg, the conveying height (H) is 900mm, the speed (V) should complete the conveying action within 5m/min, the belt width (B) is 160mm, the motor installation side is the left side (A1), the motor installation direction is downward (M2), the number of legs (N2) is 2, the distance from the legs to the motor end (D) is 500, and the leg spacing (E) is 2000. Based on these conditions, the selected model is: AMT05 - 02A - L3000 - F60 - H900 - V5 - B160 - A1 - M2 - N2 - D500 - E2000.
*Adequate performance margin should be reserved during design and selection.
V. Maintenance
Regularly clean the dust on the mechanism, and try to avoid using it in a humid environment. It is recommended to perform maintenance at least once a month.
(1) Wipe the flat belt clean with a clean cloth, and check whether the belt is cracked and whether there are tears at the edges.
(2) Wipe the oil stains at the bearing position clean with a clean cloth and add new lubricating oil.
(3) Check whether the belt driving the motor and the drum is cracked and whether the belt teeth are normal.
VI. Common Reasons for Belt Deviation
Belt deviation during the operation of the belt conveyor is one of the most common faults. There are various reasons for belt deviation, and the main reasons are low installation accuracy and poor daily maintenance. During the installation process, the head and tail drums and the intermediate idlers should be on the same center line as much as possible and parallel to each other to ensure that the conveyor belt does not deviate or deviates less. In addition, the belt joints should be correct, and the circumferences on both sides should be the same.
During the use process, if belt deviation occurs, the following inspections should be carried out to determine the cause and make adjustments. The parts often inspected and the treatment methods for belt deviation of the conveyor belt are as follows:
(1) Check the non - coincidence degree between the transverse center line of the idler and the longitudinal center line of the belt conveyor. If the non - coincidence degree value exceeds 3mm, the idler group should be adjusted using the elongated mounting holes on both sides of the idler group. The specific method is that the side of the idler group to which the conveyor belt deviates should be moved forward in the direction of the conveyor belt's advancement, or the other side should be moved backward.
(2) Check the deviation value of the two planes where the bearing seats of the head and tail frames are installed. If the deviation of the two planes is greater than 1mm, the two planes should be adjusted to be in the same plane. The adjustment method for the head drum is: if the conveyor belt deviates to the right side of the drum, the bearing seat on the right side of the drum should be moved forward or the bearing seat on the left side should be moved backward; if the conveyor belt deviates to the left side of the drum, the bearing seat on the left side of the drum should be moved forward or the bearing seat on the right side should be moved backward. The adjustment method for the tail drum is just the opposite of that for the head drum.
(3) Check the position of the materials on the conveyor belt. If the materials are not centered on the cross - section of the conveyor belt, it will cause the conveyor belt to deviate. If the materials are biased to the right, the belt will deviate to the left, and vice versa. During use, the materials should be centered as much as possible. To reduce or avoid such belt deviation, a baffle can be added to change the direction and position of the materials.





